|
|
Trophic Levels
On the land the typical Trophic Levels pattern is:
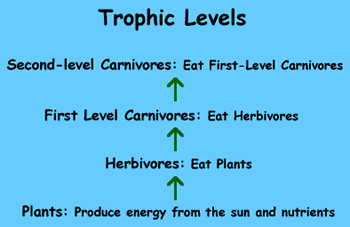
In the ocean, and on intertidal shores, this Trophic Levels pattern is a little different. There are a few other important sources of food to be taken into consideration.
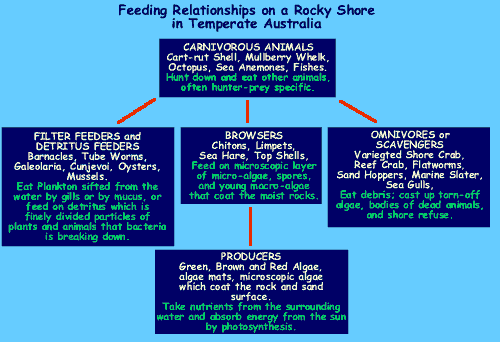
Firstly, there is Plankton which has animal, both very small and some large, and single-celled plant components. Plankton occurs in absolutely countless numbers and volume. In southern waters, it is the energy engine that drives much of the Marine Food Web.
Then there is detritus, which is the broken down ooze of dead and decaying plant and animal remains, being fed on by bacteria. Many animals are adapted to feeding on detritus, such as the Shore Crabs and many worms. The bacteria which eats the detritus is also another very important source of food. Detritus is left as a thin film on a shore when the tide receeds.
Along with detritus, more bulky debris consisting of birds and fish carcases, torn off algae clumps, and all sorts of rubbish, also left by the tide.
Nutrient
Absorbers
Grazers & Browsers
Suspension Feeders
Deposit Feeders
Carnivores
Omnivores
Trophic Levels
Energy Pyramid
Home
Page
Taxonomy
Biogeography
Rocky Shores
Tidal Levels
Intertidal Zonation
Environmental Factors
Biological
Factors
Feeding Relationships
Activities
Glossary
References