|
|
Decapod Crabs
Along the Eastern Warm Temperate Zone in south-eastern Australia on rocky ocean shores, there are many types of crab from different families. Typical shore crabs belong to two major groups; the Grapsid Shore Crabs and the tall-eyed Ocypode Crabs.
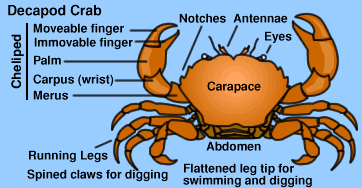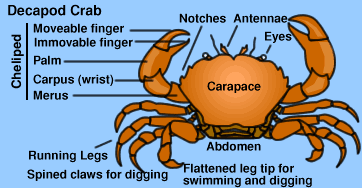
Grapsid Shore Crabs - Grapsidae
The Grapsids have invaded the largest number of shore habitats. They may be distinguished by their broad fronts, short eyes and almost square-shaped carapace.
Some grapsids can leave the water for long periods of time. As the deoxygenated and carbon dioxide loaded water is expelled from the gill chambers, it is spread over spongy areas on either side of the mouth where it picks up fresh oxygen.
Appendages at the entrance of the gill cavity near the base of the claws (chelipeds) drives the oxygen recharged water back to the gills.
Most grapsids have equal-sized chelae (claws), unless one has been broken off and is regrowing. Male grapsids usually have much larger chelae than females of the same species.
Some grapsid shore crabs which are found along our shores are:
![]() Variegated
Shore Crab, Leptograpsus variegatus
Variegated
Shore Crab, Leptograpsus variegatus
![]() Red
Bait Crab, Plagusia chabrus
Red
Bait Crab, Plagusia chabrus
![]() Sowrie,
Plagusia glabra
Sowrie,
Plagusia glabra
![]() Smooth
Shore Crab, Cyclograpsus audouinii
Smooth
Shore Crab, Cyclograpsus audouinii
Ocypodid Shore Crabs - Ocypodidae
The other major group of shore crabs are the Ocypodids, These are the Ghost Crabs and Fiddler Crabs and relatives. They are mostly all tall-eyed, with the bases of their eyes close together at the front of the carapace. Ocypodid crabs live on sandy beaches, mudflats and in mangrove swamps. They are active burrowers and many live in colonies. The male Ghost Crabs and especially the Fiddler Crabs have unequal sized chelae.
Ocypodids are not normally found on rocky ocean shores.
Spider Crabs - Majidae
These Majidae crabs are commonly known as the Spider Crabs. The seaweed crabs of this family are covered with long hooked hairs, which allow the crab to snip off living pieces of algae and attach them to the hairs. A decorated seaweed crab with algae, sponges and other marine growths is excellently camouflaged. It only gives itself away when it moves.
One seaweed crab found in the intertidal zone in south-eastern Australia is the:
![]() Seaweed
Decorator Crab, Naxia tumida
Seaweed
Decorator Crab, Naxia tumida
Black Fingered Crabs - Xanthidae
The black-fingered crabs are the largest group of crabs in Australian seas. Xanthids are very common in tropical waters, especially on the Great Barrier Reef.
Most members of the group are almost oval in shape, being slightly wider than long. The distinguishing feature of the group, is the dark coloured fingers of the chelae.
The most common black-fingered crab on rocky ocean shores in south-eastern Australia is the:
![]() Reef
Crab, Ozius truncatus
Reef
Crab, Ozius truncatus
Swimming Crabs - Portunidae
The portunid swimming crabs have a broad carapace and flattened hind legs which form swimming paddles and sometimes digging spades. None of the portunids come out onto the shore, but they do enter shallow water to hunt for live food. The most common estuarine swimming crab is the Blue Swimmer Crab, Portunus pelagicus.
On the rocky ocean shore one of the most attractive crabs is the:
![]() Tubercled
Shore Crab, Nectocarcinus tuberculosus
Tubercled
Shore Crab, Nectocarcinus tuberculosus
Regrowth of Limbs
Decapod crabs can regrow their limbs if they are broken off. In fact there is a special "weakness plane" across the leg, so that if a predator grasps the limb, the leg breaks off, and special muscles contract and pinch off the nerves and stem the loss of fluid. It takes about six or so moults to regrow a severed limb.
| For more information on Crustaceans visit MESA Crustaceans |
Topics
Environmental
Factors
Latitude
Water Currents
Wind
Effects
Wave Strength
Tide Effects
Desiccation
Substrate
Salinity
Home
Page
Taxonomy
Biogeography
Rocky Shores
Tidal Levels
Intertidal Zonation
Environmental Factors
Biological
Factors
Feeding Relationships
Activities
Glossary
References
 Life
on Australian Seashores
Life
on Australian Seashores
by Keith Davey (C) 2000
Learning Consultant
- Media
The University of Newcastle
email at australian_seashores@hotmail.com
Scientific Consultant: Phil
Colman
site created 01.01.98 : updated 01.04.2000
