Mariculture in Tasmania
Mussels
Australian exports of mussels are small, with less than 1%t of production exported. Exports in 2001-02
were 3.3 tonnes of live, fresh or chilled product with
an export value of $27,000, and 21.8 tonnes of frozen,
dried or salted product with an export value of $139.000. Australian mussels are exported to
various countries in Europe, Asia and North America.
Mussels are farmed in all Asutralian states except Queensland. Victoria and Western Australia are the largest producers in 2001-02, Victoria
produced 1,580 tonnes of mussels valued at $3.7 million at the farm gate, and
Western Australia produced 989 tonnes valued at $2.8 million. In Tasmania, mussels are produced on the east and south east coasts. Production in 2001-02 was 217 tonnes valued at around $760 000 at the
farm gate.
The two main species farmed are Blue Mussels (Mytilus edulis) and Tasmanian Blue Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis). |

|
| |
|
Mussel Biology
Wild mussels are found in bays and estuary systems attached to rocks, wharfs and jetties in the low and mid intertidal zones. They are usually clumped together on wave-washed rocks. Clumping together helps protect them from the wave action.
Mussels are bivalves molluscs. The external shell is made of two hinged halves or "valves". The valves are joined together on the outside by a ligament, and can be closed by strong internal muscles. Mussel shells have a number of functions, including support for internal organs, protection from predators and protection against drying out. The foot is tongue-like in shape, it has a groove in it called the byssus pit. This pit secretes a sticky material which hardens on contact with seawater, This material forms strong, elastic threads that hold the mussel tightly to a surface. This is known as the mussel's beard and needs to be removed by hand before the mussel is cooked. |
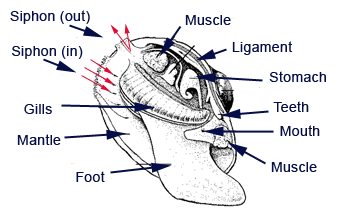
|
They are filter feeders, pumping water through a siphon into gill filaments which filter out small food particles like phytoplankton, zooplankton and other organic material. The watse water, conatining sediment, is pumped out through another siphon while the food is retained and passed into the stomach for digestion. Marine mussels are eaten by humans, sea stars, seabirds, and by many marine snails.
Next: Mussel farming |
|