Making a crust in the southern ocean: how the creation of ocean floor and
hydrothermal black smoker vents puts aliens on our planet.
Garry Davidson, Centre for Ore Deposit Research (CODES),
School of Earth Sciences, University of Tasmania.
|
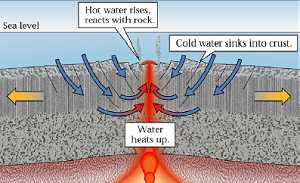
Seventy percent of our planet is made up of oceanic crust – very different stuff to the material that makes up the continents. This crust is created along vast mountain chains of fissure volcanoes, which run the length of every known ocean. The fissure volcanoes are fed by magma chambers, which heat the crust around them, like under floor heaters in a cold wet kitchen.
The chemistry of the ocean is controlled by these regions, because cold seawater is drawn down into the crust around the chambers, it is heated to furnace temperatures and jets back to the ocean floor as highly modified, metal-laden, hydrothermal waters. One major modification is the loss of free oxygen and the addition of hydrogen sulfide, deadly to most organisms on Earth.
The miracle is that Nature has evolved animals and ecosystems that can not only live around these hostile submarine hot springs, they rely on the bizarre chemistry for their survival. These are truly the aliens on our planet. |
 |
| |
|
|
Australia is very fortunate in having access to a sliver of the ocean floor that has been thrust upward by geological forces to form a unique Island in our southern ocean, ie Maquarie Island. Macquarie Island is the world’s only mid-ocean ridge crust exposed above sea level outside of Iceland. It has deep levels of crust exposed and a vital place to study global processes in 3D!
Earth Scientists are stewards or caretakers of Earths’ resources and environment. They work to understand natural processes on Earth and other planets. Investigating the Earth, its soils, oceans, and atmosphere; forecasting the weather; developing land-use plans; exploring other planets and the solar system; determining environmental impacts; and finding new sources of useful Earth materials are just a few of the ways geoscientists contribute to our understanding of Earth processes and history.
Earth Scientists provide essential information for solving problems and establishing governmental policies for resource management; environmental protection; and public health, safety, and welfare. Earth Scientists are curious about the Earth and the solar system. What is the composition of other planets, and do they sustain life? How are they changing? What effects will shrinking glaciers have on the oceans and climate? What makes a continent move, a mountain form, a volcano erupt? Why did the dinosaurs become extinct? Earth Scientists are concerned about our environment. How is the global climate changing? How do Earth systems work? How and where should we dispose of industrial wastes? How can society ’s growing demands for energy and water be satisfied while conserving natural resources for future generations? As global populations increase, can we grow enough food and fibre to sustain them? |
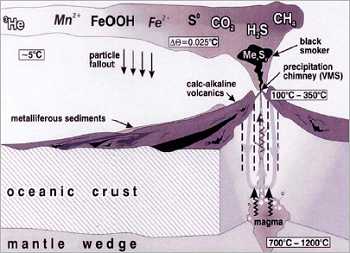
Drawings from the MESA Conference 2003 presentation
and the bottom one Massoth et al. (2002) |
| |
|

Black smoker- East Pacific Rise,
from the Conference Presentation
|
The Earth is an outdoor laboratory filled with opportunities to observe Earth processes in action. By applying their knowledge of forces and factors that shape the Earth, Earth Scientists seek to reconstruct the past and anticipate the future.
Tasmania is an ideal place to study geology. We have one of the best School of Earth Sciences in Australia, with an international reputation for advanced research and a Special Research Centre for Ore Deposit Research. Also, we have a natural laboratory on our very doorstep; Tasmanian geology is impressive and varied, and on the west coast we have a series of world class ore deposits readily available for study.
For more information Contact the University of Tasmania and ask for the ‘Why Earth Science: An Introduction to Earth Sciences CD'. |
|