Module 5
Investigating Coastal and Marine Environments
through Science
|
Resources |
| Resource 1 |
Science - A Curriculum Profile for |
Resource 2A |
Investigating Plankton from the Mangroves |
Resource 2B | Change and the Mangroves |
| Resource 2C |
Field Excursion to the Mangroves |
Resource 2D |
Investigating Common Barnacles in |
Resource 3A | Analysing Science Activities |
| Resource 3B | "Working Scientifically" | Resource 4A | The Real Distributions of Mangrove Oysters | Resource 4B | Design Your Own Field Trip |
Resources
Resource 1
Science - A Curriculum Profile for Australian Schools
| Source: Department of Environment, Sport and Territories (1996) Coast and Marine Schools Project. Stage 1 - Part 4: Links with Curriculum, Final Report, Canberra, Table 4.A.1. |
| Level | Planning investigations | Conducting investigations | Processing data |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
|
|
|
| Level | Evaluating Findings | Using Science | Acting Responsibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
|
|
|
Resource 2A
Investigating Plankton from the Mangroves
| Source: Adapted from Seaweek: Exploring the Deep Sea, Seaweek Secondary School Kit, Levels 6-7, Marine Education Society of Australasia, Inc., Brisbane, 1997. |
Plankton are producers and lower order consumers in the carbon cycle.
A plankton trawl can be carried out from a jetty inside a mangrove forest
at dusk. Once collected they should be transferred to seawater in a tank
and can be observed using a dissecting microscope.
Activities
- Draw two zooplankton and phytoplankton species that you find in the
plankton samples.
- Explain how plankton move in the water.
- Draw a simple food chain using the species identified from the study
area?
- What human activities may affect the number of plankton in your sample?
Resource 2B
Change and the Mangroves
| Source: Adapted from Ross, P.M. (1995) Mangroves: A Resource, Environmental Protection Authority, Sydney. |
- Background Information
- Mangroves are fragile and lots of human activities could seriously
threaten them. Now that you have done some reading about the mangroves
you have been sent out to check the state of the mangroves at different
places along the Australian coast. Try and think about some reasons
for what you see.
- Location 1
- You walk through the mangrove forest and onto the mudflat and you
only see one or two crabs. It is winter.
Cause:
Effect on the environment:
Should anything be done to help the situation? What?
- Location 2
- You observe that many mangrove trees have lost their leaves. It is
summer time and the roots of the mangrove trees look healthy.
Cause:
Effect on the environment:
Should anything be done to help the situation? What?
- Location 3
- You record that the whole of the area past the mangrove trees has
an enormous amount of algae. It is February.
Cause:
Effect on the environment:
Should anything be done to help the situation? What?
Resource 2C
Field Excursion to the Mangroves
- Junior Secondary
| An Extract of a Field Excursion to the Mangroves - Junior Secondary Source: Adapted from Ross, P.M. (1995) Mangroves: A Resource, Environmental Protection Authority, Sydney. |
Saltmarsh
- Draw the red plant which is found in this area.
- Some of the snails are found underneath these plants.
- How do they feel? (smooth, bumpy etc.)
The Mangrove Forest
- Draw a leaf of the main mangrove tree in the area. Find out from an identification book the name of this tree.
- Lick the leaf. How does it taste?
- Name some of these plants and animals.
- Run a transect, from the land to the sea run a transect and every 10 m put down the 1 m quadrat and count the animals and plants under the quadrat.
- Measure the air and soil temperature at each quadrat.
- Fill in table below.
Back at School
- Graph your results (number of organisms and temperature).
- Did the animals or plants change in number throughout the forest?
- Where were the animals in greatest abundance?
- Think of some reasons for this and write them down.
| Organism/ Temperature | Quadrat 1 | Quadrat 2 | Quadrat 3 | Quadrat 4 | Quadrat 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Resource 2D
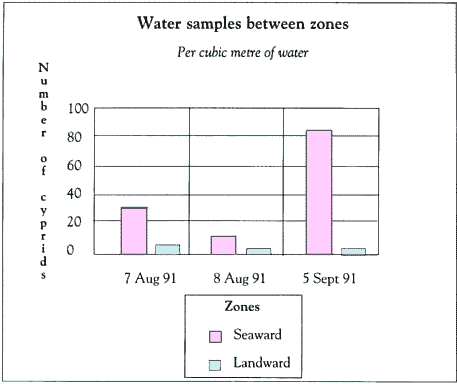
Investigating Common Barnacles in the Mangroves
| Source: Adapted from Ross, P.M. (1995) Mangroves: A Resource, Environmental Protection Authority, Sydney. |
Background Information
If you enter a mangrove forest and look at the barnacles on the bark of the trees, it seems that they are more common on the bark of trees which are closest to the sea than on trees which are closest to the land. Barnacles have parts of their life cycle which swim in the water feeding on phytoplankton. These stages are known as larvae. The last stage is called a cyprid. It has a specific function to return to the forest and find a place on a mangrove tree on which to stick. Samples were taken of the water column by using a plankton net. Data was collected on how many cyprids were in the water column. The results were graphed. What generalisations can you make?